Stop Manual Checks: Automating DORA Compliance for Cloud Dependencies
Financial services organizations face increasing pressure to comply with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) while managing complex cloud infrastructures. Manual compliance checks for third-party dependencies are no longer sustainable. This guide explores how to automate DORA third-party risk management, ensuring continuous compliance without the overhead of manual processes.
Understanding DORA's Third-Party Requirements
DORA mandates that financial entities maintain operational resilience by managing risks associated with their ICT third-party service providers. This includes cloud services, SaaS applications, and any external dependencies that could impact service delivery.
The regulation requires organizations to:
Maintain an up-to-date register of all third-party ICT providers
Continuously monitor the performance and availability of critical dependencies
Document and assess concentration risks
Implement incident response procedures for third-party failures
Provide evidence of ongoing risk management activities
The Challenge of Manual Compliance
Manual compliance checking creates several operational challenges:
Time-Intensive Processes: Security and compliance teams spend hours checking vendor status pages, documenting incidents, and updating risk registers. This manual work diverts resources from strategic initiatives.
Delayed Detection: Manual checks happen periodically, meaning critical vendor issues might go unnoticed for hours or even days. This delay increases both operational and compliance risks.
Incomplete Coverage: With dozens or hundreds of cloud dependencies, manual monitoring inevitably misses important events. Teams simply cannot check every vendor status page continuously.
Documentation Gaps: Manual processes often result in inconsistent documentation, making it difficult to demonstrate compliance during audits.
Building an Automated Compliance Framework
Automating DORA third-party risk management requires a systematic approach that combines monitoring, documentation, and risk assessment.
1. Automated Dependency Discovery
Start by implementing automated discovery tools that identify all cloud dependencies across your infrastructure. This includes:
Direct cloud service providers (AWS, Azure, GCP)
SaaS applications used by different departments
API dependencies in your applications
Infrastructure services like CDNs and DNS providers
Automated discovery ensures your third-party register remains complete and current without manual inventory efforts.
2. Continuous Monitoring Implementation
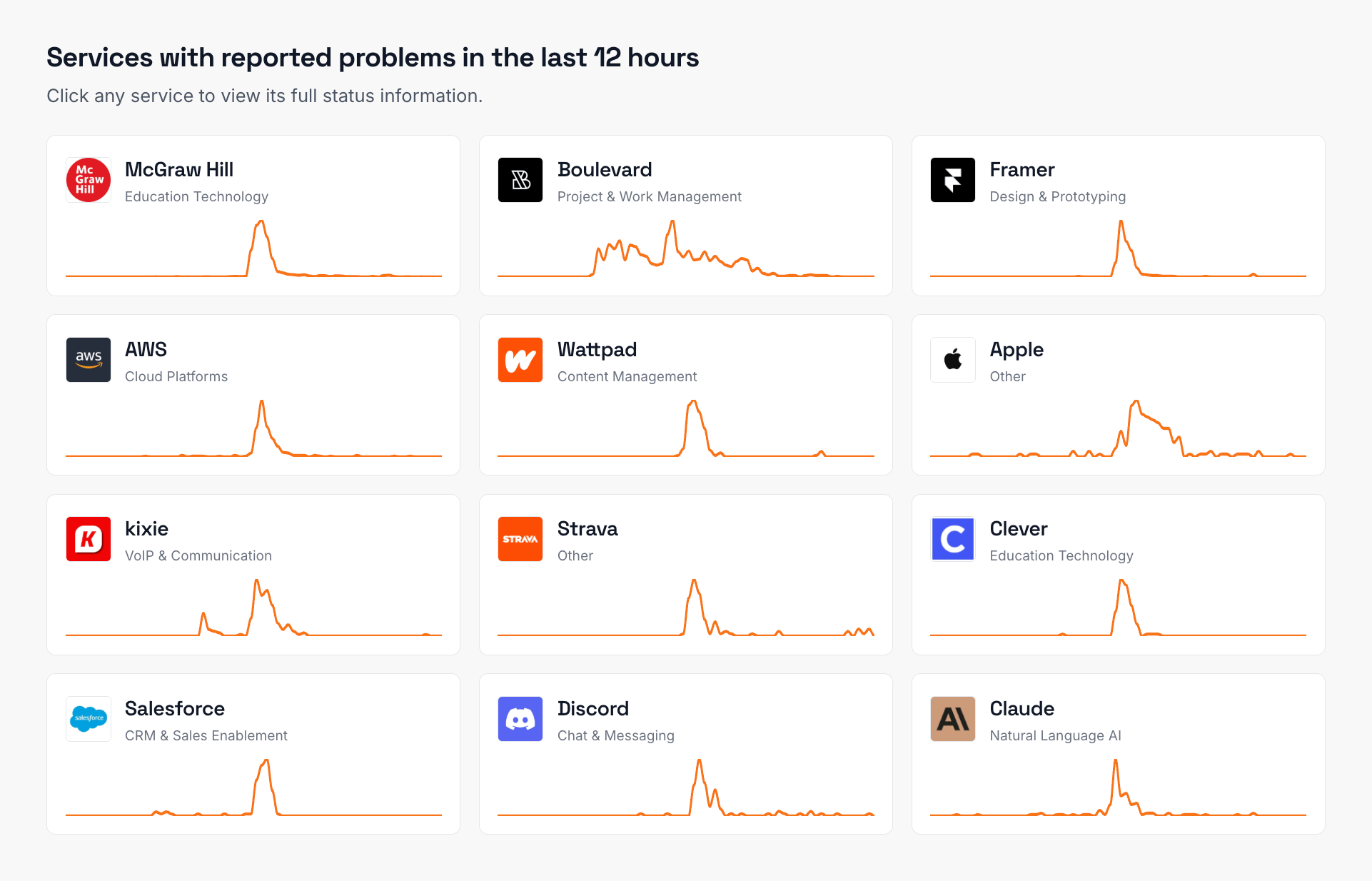
Replace manual status checks with automated monitoring that tracks all your dependencies 24/7. A comprehensive third-party monitoring dashboard centralizes this information, providing real-time visibility into vendor health.
Key monitoring capabilities include:
Real-time status tracking for all critical vendors
Automated incident detection and alerting
Performance metrics collection
Historical data retention for compliance reporting
3. Risk Scoring Automation
Develop automated risk scoring models that evaluate each third-party dependency based on:
Service criticality to your operations
Historical reliability metrics
Concentration risk factors
Alternative vendor availability
Automated scoring helps prioritize risk management efforts and demonstrates proactive compliance to regulators.
4. Incident Response Automation
When vendor incidents occur, automated workflows ensure consistent, compliant responses:
Immediate notification to relevant teams
Automatic creation of incident records
Triggering of predefined mitigation procedures
Documentation of all response activities
This automation ensures DORA's incident management requirements are met consistently, regardless of when issues occur.
Technical Implementation Strategies
Successful automation requires the right technical architecture and tools.
API-First Monitoring
Leverage vendor APIs and status feeds to collect real-time availability data. This approach provides more timely and accurate information than manual checks. Many organizations use specialized monitoring platforms that aggregate multiple vendor status feeds into a single interface.
Event-Driven Architecture
Implement event-driven systems that automatically respond to vendor status changes. When a critical dependency experiences issues, your system should:
Log the event with timestamp and details
Assess potential impact on your services
Notify appropriate teams based on severity
Update risk registers automatically
Integration with Existing Tools
Connect your automated monitoring to existing ITSM and GRC platforms. This integration ensures compliance data flows into your established processes without creating new silos. Consider how incident alert management systems can support both operational response and compliance documentation.
Measuring Compliance Effectiveness
Automation enables continuous measurement of your DORA compliance posture:
Coverage Metrics: Track the percentage of third-party dependencies under automated monitoring. Aim for 100% coverage of critical and important vendors.
Response Time Metrics: Measure how quickly your organization detects and responds to vendor incidents. Automated systems should significantly reduce mean time to detection (MTTD).
Documentation Completeness: Assess the quality and completeness of automatically generated compliance documentation. Ensure all required DORA elements are captured.
Risk Trend Analysis: Use automated data collection to identify trends in third-party risks over time. This analysis supports strategic vendor management decisions.
Common Implementation Pitfalls
Avoid these common mistakes when automating DORA third-party risk management:
Over-Automation: Not every process needs full automation. Focus on high-value, repetitive tasks first.
Ignoring Data Quality: Automated systems require clean, accurate data. Invest in data validation and cleansing processes.
Insufficient Testing: Thoroughly test automated workflows, especially incident response procedures, before relying on them for compliance.
Neglecting Human Oversight: Automation should augment human decision-making, not replace it entirely. Maintain appropriate oversight and review processes.
Future-Proofing Your Compliance Strategy
As DORA requirements evolve and your organization grows, your automated compliance framework must adapt:
Design modular systems that can incorporate new monitoring requirements
Build flexibility into risk scoring algorithms
Maintain vendor-agnostic approaches to avoid lock-in
Regularly review and update automation rules
Organizations that invest in robust automation today will find it easier to adapt to future regulatory changes while maintaining operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What specific DORA requirements can be automated for third-party risk management?
Key DORA third-party risk management requirements that can be automated include continuous monitoring of vendor availability, automatic incident detection and documentation, risk scoring updates, and compliance reporting generation. Automation is particularly effective for maintaining the ICT third-party register and tracking concentration risks across your vendor portfolio.
How long does it typically take to implement automated DORA compliance monitoring?
Implementation timelines vary based on organizational complexity, but most financial institutions can deploy automated third-party monitoring within 4-6 weeks. Full automation including risk scoring, incident response workflows, and integrated reporting typically requires 3-4 months. Starting with critical vendors and expanding coverage gradually reduces implementation risks.
What are the cost implications of automating DORA compliance?
While initial setup requires investment in monitoring tools and integration work, automation is estimated to reduce operational compliance overhead by up to 40-60% within the first year. Savings come from reduced manual effort, faster incident detection, and avoided regulatory penalties. Most organizations see positive ROI within 6-9 months of implementation.
Can automated monitoring replace all manual DORA compliance activities?
Automation significantly reduces manual work but cannot eliminate it entirely. Human oversight remains essential for strategic vendor relationships, complex risk assessments, and regulatory communications. Automation handles routine monitoring, data collection, and initial incident response, freeing compliance teams to focus on higher-value activities.
How do we ensure our automated system meets DORA audit requirements?
Design your automation with audit trails built in from the start. Every automated action should generate detailed logs including timestamps, data sources, and decision criteria. Regular testing of automated processes, documented procedures, and periodic manual reviews demonstrate to auditors that your automated controls are effective and reliable.
What happens if our automated monitoring system fails during a critical vendor incident?
Implement redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous monitoring. This includes backup monitoring services, alternative data sources, and manual escalation procedures. Regular disaster recovery testing validates these failsafes. Document your continuity plans clearly to satisfy DORA's operational resilience requirements.
 Nuno Tomas
Founder of IsDown
Nuno Tomas
Founder of IsDown
Stop wasting hours on 'is it us or them?'
Unified vendor dashboard
Early Outage Detection
Stop the Support Flood
Related articles
Never again lose time looking in the wrong place
14-day free trial · No credit card required · No code required